Project 2Climate change and global risk assessment
Results of FY 2014
One of our objectives is to globally clarify the climate risks including not only the negative but also the positive impacts. Therefore, experts in various fields participating in our project have reviewed the latest research and compiled a comprehensive list of climate risks. We have also prepared a comprehensive list and drawn a complex diagram of the causal relationships among climate risks. Existing reports such as the IPCC AR5 have, until now, described climate risks in separate categories, but the cross-sectoral causal relationships have not been systematically summarized. We expect that our comprehensive list and network diagram will not only contribute to a global understanding of the complete picture of climate problems, but it will also provide useful information.
By investigating the causal relationships among climate risks we have been able to clarify in this research the overall picture of climate risks. In Figure 1, we have summarized the impacts that changes in the climate system have on the natural environment, social systems, security, human activities and ecosystems. In Figure 2, the causal relationships among risks in connection with food are shown. Here, only risks where food is either the cause or the effect are shown, and the causal relationships among risks are illustrated with connecting arrows.
When the climate system changes, it causes a decline in crop production and changes in the natural capital. These changes alter the social system, resulting in an instable food supply and deteriorated food security. These changes also affect human activities in the form of an increase in malnutrition and intensification of human migration. However, depending on the place, these changes may also have a positive impact such as increase in crop productivity. In the near future we plan to add more quantitative information on the size of the damage and benefits along with the occurrence probability, as well as information on the effects of countermeasures.
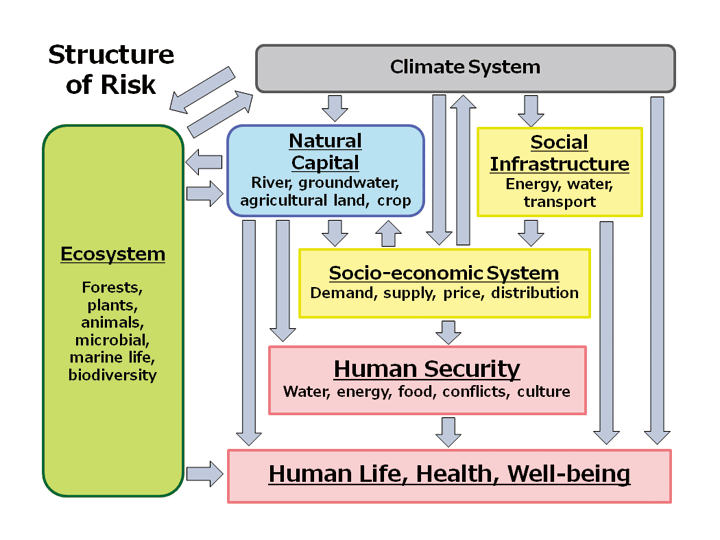
Figure 1.Comprehensive figure over casual relationships among climate risks. The impacts of changes in the climate system can be classified into “Natural capital” (light blue), “Ecosystem” (green), “Social infrastructure” (yellow), “Human security (water/food/energy security), and Human life, health and well-being” (pink). These impacts affect each other mutually.
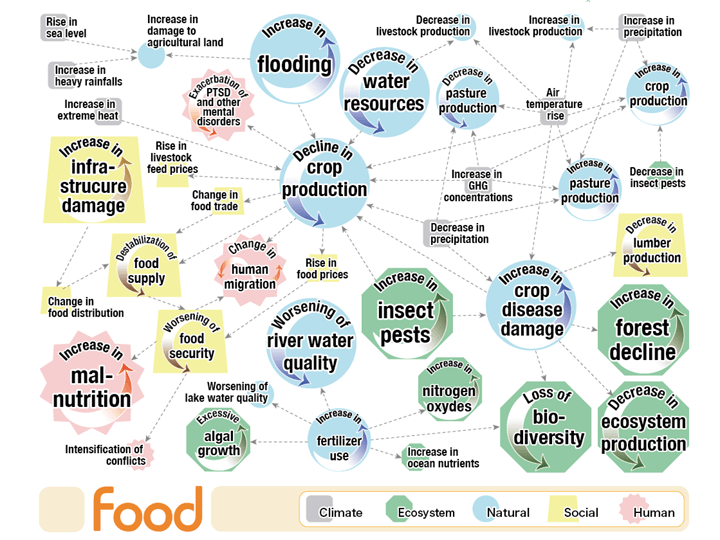
Figure 2.Food-related risks among climate change relationships. The relationships between risks are marked with arrows. Only relationships where food is involved in either the cause or the effect are illustrated. Other risks, such as water resources, energy, disasters and society, health, ecosystems and tipping elements are illustrated in different network figures. The risks are marked in three different sizes. More than eight risks among the causal relationships summarized in the present study are shown as large, more than four as medium and only less than three as small risks. The color code in the figure is based on the colors of the total risk structure in Figure 1. However, factors that are related to changes in the climate system and are independent of causal relationships are denoted as small grey items.